Discover History and Mythology of Solar Eclipses in China and how it makes us connect to what our ancestors might have felt and experienced.
On July 22, 2009, we were visiting the Three Gorges Dam, a hydroelectric gravity dam that spans the Yangtze River by the town of Sandouping, in Hubei province, China.
In this Article
The Three Gorges Dam, is the world’s largest power station in terms of installed capacity and a good place to watch the total solar eclipse – the longest of the 21st century. It lasted up to a maximum of 6 minutes, 39 seconds according to NASA.
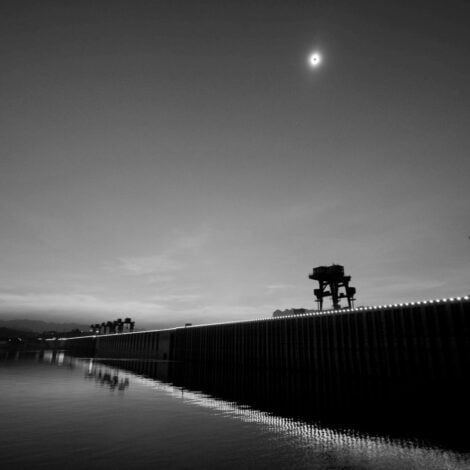

It is a once-in-a-lifetime phenomenon: we grab our darkened glasses, following reminders that viewing with the naked eye could damage our eyesight.
The light of day begins to fade in the middle of the day. Looking up, we catch a glimpse of what looks like a disk of pure blackness sliding across the face of the sun.
Soon the blackness has almost completely covered the sun, and dusk is falling over the land. The air cools. The birds are silent and still. Streetlights are turned on. Fireworks lighten up the darkness, silence is broken.
Feelings as the light drops away: Is an eclipse frightening? Beautiful? Or both at once?
The Solar Eclipse of 22nd July 2009
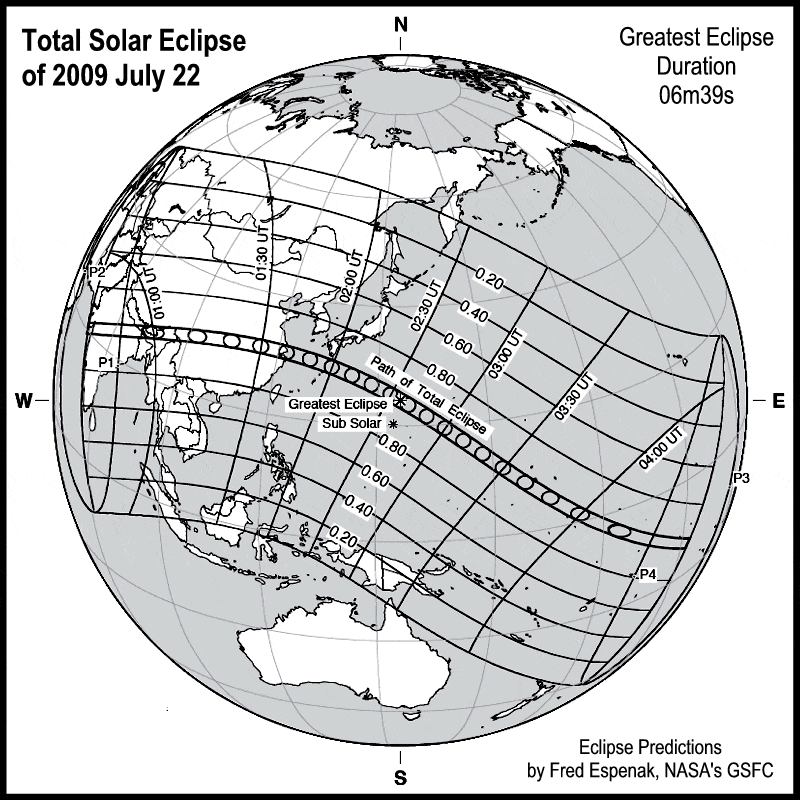
As the Earth and moon sweep through space in their journey around the sun, the three bodies align in such a way that the Earth passes into the shadow of the moon. We witness a sun that is gradually covered and uncovered by the moon’s disk, without the sun’s light, the sky darkens enough for stars to be seen and the sun’s corona makes a halo around the moon– a spectacular celestial event.
The word eclipse comes from a Greek word meaning “abandonment.” Quite literally, an eclipse was seen as the sun abandoning the earth.
The eclipse traveled half the globe and was visible along a roughly 250 km (155 miles)- wide corridor. The phenomenon began at dawn over the western coast of India, it moved east across Nepal, Burma, Bangladesh and Bhutan and then along China’sYangtze river valley.
Monsters try to devour the Sun- worldwide
Eclipses of the Sun are awe-inspiring phenomena. It is no wonder that in many early cultures they were believed to be the end of the world or bad omens. Seeing one makes me connect to what our ancestors might have felt and experienced.
In China, India, southeastern Asia and in Peru there were beliefs that dragons or demons attack the Sun during eclipses. In North America, dogs and coyotes; in South America, big cats like pumas; in Vietnam, a very large frog tries to swallow the sun.
The ancient Egyptian myth of the snake Apep that attacks the boat of the Sun god is believed to refer to solar eclipses.
The Ch’orti’, indigenous Mayas, believed an eclipse of the sun that lasts more than a day will bring the end of the world, and the spirits of the dead will come to life and eat those on earth.
The Florentine Codex, an ethnographic study of 16th-century Aztecs in Mexico, described a solar eclipse in particularly vivid terms:
There were a tumult, and disorder. All were disquieted, unnerved, frightened. Then there was weeping. The common folk raised a cup, lifting their voices, making a great din, calling out shrieking. People of light complexion were slain as sacrifices; captives were killed. All offered their blood.
They drew straws through the lobes of their ears, which had been pierced. And in all the temples there was the singing of fitting chants; there was an uproar; there were war cries. It was thus said: “If the eclipse of the sun is complete it will be dark forever. The demons of darkness will come down. They will eat men!”
The Chinese and the Incas tried to frighten these monsters away, by banging pots, chanting or shooting into the air.
But the Indians have a different attempt by immersing themselves in holy water, the Ganges. They performed this religious ritual to help the Sun struggle against the decapitated head of a Hindu demon, Rahu.
The god Vishnu, warned by the sun and the moon, caught Rahu drinking the elixir of life and as punishment sliced off the demon’s head before the elixir passed through his throat. The immortal head takes his revenge on the celestial bodies by devouring them, but because he has no body, they re-emerge after he swallows them.
Muslims pray five times daily, but during eclipses they specially perform the “eclipse prayer”. This is one of the traditions of Prophet Mohammad, Peace Be Upon Him (PBUH). The purpose of this prayer is to remember the might and gifts of Allah the Creator.
Ancient Chinese believed eclipses were caused by giant animals
A mystical dragon or celestial dog in the sky eating up the Sun explains the Chinese word for eclipse, which is 日食 (re shi), meaning ‘sun eat’.

LEGEND: The Sun-eating Dragon
The ancient Chinese believed that solar eclipses occur when a legendary celestial dragon devours the Sun. They also believed that this dragon attacks the Moon during lunar eclipses.
It was a tradition in ancient China to bang drums and pots, use firecrackers or even shoot arrows into the sky, all in an effort to frighten away the dragon.
Even more recently, in the nineteenth century, the Chinese navy fired its cannons during a lunar eclipse to remember the old custom.
LEGEND: The Sun- eating Dog- Tian Gou 天狗 (tiān gǒu)

Another tale tells us, that ancient Chinese believed that solar and lunar eclipses were caused by a hungry dog called Tiangou or Tian Gou (“heaven dog”), trying to devour the sun or moon. Luckily, Tiangou was always stopped by the god of childbirth, Chang Xian, an expert archer.
Since eclipses were omens of great change, fending off sun-eating dogs was serious business. As such, royal astronomers at the emperor’s court were charged with shooting arrows, banging pots or even used firecrackers and making whatever noise they could to scare off this eclipsing canine.
Despite their efforts, the tale of the heavenly dog has persisted. 20th century Chinese poet Guo Moruo wrote on Tian Gou:
I am a heavenly dog!
I eat up the Moon,
I eat up the Sun.
I eat up all the planets, I eat up the universe.
I become what I am!
Originally seen as an animal that can counter evil, Tian Gou somehow became the synonym to comets which are seen as bad omen in ancient China.
Chang Xian the archer and fertility

There is another story concerning how Zhang Xian or Chang Xian (an immortal in Chinese lore) shot the Heavenly Dog.
In this story, the Heavenly Dog was obstructing the constellations from going to the mortal realm as children.
When Chang Xian shot the Heavenly Dog and made it run away, the people were then able to get children and as a result, Chang Xian was known as “the children-giving Chang Xian”.
In China the belief that
eclipses herald change
coexisted with the scientific explanation.
COSMOGONY: P’an Ku 盘古
The most conspicuous figure in Chinese cosmogony is P’an Ku or Pan Gu.
He it was who chiseled the universe out of Chaos. According to Chinese idea, he was the offspring of the original dual powers of Nature, the yin and the yang -, which, having in some incomprehensible way produced him, set him the task of giving form to Chaos and
“making the heavens and the earth.”
Some accounts describe him as the actual creator of the universe, — “the ancestor of Heaven and earth and all that live and move and have their being.” ‘P’an’ means ‘the shell of an egg,’ and ‘Ku’ ‘to secure,’ ‘solid,’ referring to P’an Ku being hatched from out of Chaos and to his settling the arrangement of the causes to which his origin was due.
The characters themselves may, however, mean nothing more than ‘Researches into antiquity,’ though some bolder translators have assigned to them the significance if not the literal sense of ‘aboriginal abyss,’ or the Babylonian Tiamat, ‘the Deep.’

In some of the pictures P’an Ku is represented, as holding the sun in one hand and the moon in the other. Sometimes they are in the form of those bodies, sometimes in the classic character.
The legend says that when P’an Ku put things in order in the lower world, he did not put these two luminaries in their proper courses, so they retired into the Han Sea, and the people dwelt in darkness. The Terrestrial Emperor sent an officer, with orders that they should come forth and take their places in the heavens and give the world day and night. They refused to obey the order.
They were reported to Ju Lai; P’an Ku was called, and, at the divine direction of Buddha, wrote the character for ‘sun’ in his left hand, and that for ‘moon’ in his right hand; and went to the Han Sea, and stretched forth his left hand and called the sun, and then stretched forth his right hand and called the moon, at the same time repeating a charm devoutly seven times; and they forthwith ascended on high, and separated time into day and night.
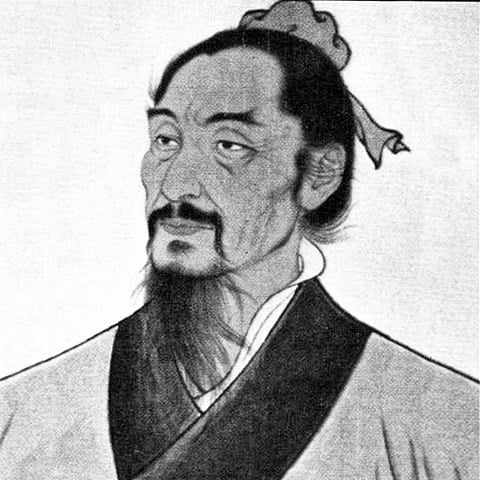

Mo Di 墨翟and Creation
Mo Di, or Mo Tzŭ 墨子 (fifth and fourth centuries BC), generally known as Mo Ti, Mu Tzŭ, Mozi or “Master Mo,” is best remembered for being the first major intellectual rival to Confucius and his followers. In his philosophy , we find the idea of creation:
“It was”, he said, “Heaven” (which was anthropomorphically regarded by him as a personal Supreme Being) who “created the sun, moon, and innumerable stars.”
Mythology of Solar Eclipses: The Sun and the Moon
The Chinese use a calendar system based on the phases of the moon (measured through observing the position of the stars in the twenty-eight mansions) and the time of the solar year, or season.
Over generations of observation, astronomers discovered a relationship we now know as the Saros cycle, a cycle in which sun, moon and earth are aligned in a particular way approximately every 18 years, 11.3 days. This enabled them to predict solar and lunar eclipses with some accuracy but it was not an infallible system.

The sun and moon have always had a special significance in Chinese folklore and various symbolism and myths surround them. The mid-Autumn, or Moon Festival is perhaps the second most important traditional festival in China after Chinese New Year.
It is held on the fifteenth day of the eighth lunar month when the moon is said to be at its largest, roundest, and brightest of the year.
The shape of the moon is said to represent completeness and perfection and its celebration is an important family occasion each year. Special round cakes, called moon cakes 🥮, are made to eaten during the festival.
The sun and moon have developed a particular iconography in China.
Fuxi and Nüwa holding the sun and moon disc with the golden crow
Fuxi and Nuwa are Chinese demigods and culture heroes who are associated with origin legends and the gifting of knowledge and the arts to mankind. The pair have snake-like (anguipede) lower extremities, human upper bodies, and wings. They are thought of as brother and sister, husband and wife, and Sage Kings of the first human (Chinese) society.
They are associated with the moon (Nuwa) and sun (Fuxi), as seen here, and are given a Daoist philosophical interpretation as inventors of the trigram and as symbols of intertwining yin and yang.
This type of Fuxi and Nuwa are found only in the Jian region of Koguryo ( territory originally belonged to Korean Goguryeo but is now part of China) and not in the murals in the Pyeongyang area. Ohoe Tomb, 6th – 7th century, Ji’an, China.
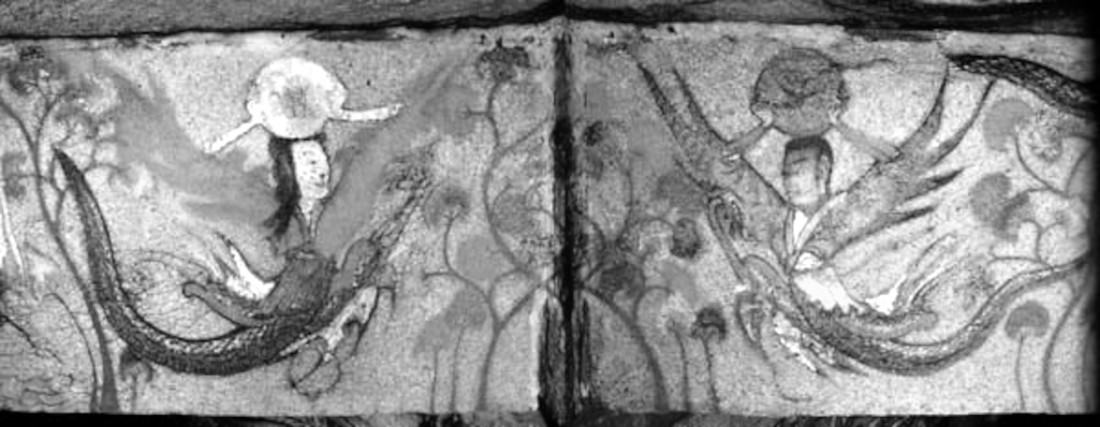
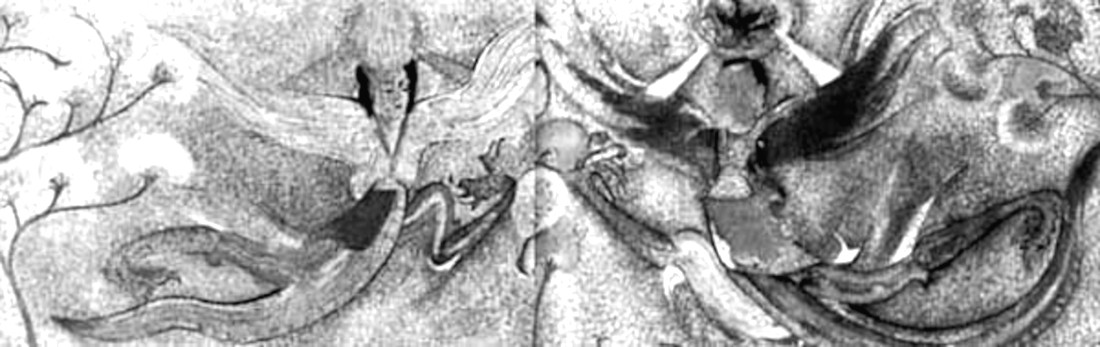
As ancient Chinese depictions show, the Chinese god of creation, Fuxi, is often depicted carrying the sun disk with the jīnwū (金烏 ‘golden crow’) while the Chinese goddess of creation, Nüwa, holds the moon disk which contains a gold-striped toad.
Brick with Fuxi and Nüwa holding the sun and moon disc.
Fuxi and Nvwa, China, collected from Chongzhou City, Sichuan, Eastern Han dynasty, 25-220 AD, tomb tile – Sichuan Provincial Museum 四川省博物院 – Chengdu, China. Photography was permitted in the museum without restriction. Public domain, edited.

THE MOON
玉兔 Yùtù
The Moon rabbit, Moon hare or Jade rabbit – 玉兔 Yùtù is a mythical animal that lives on the moon, based on pareidolic interpretations that identify the dark markings on the near side of the Moon as a rabbit or hare. The rabbit is seen pounding a pestle and mortar, or holding an egg, jumping or running.
If you look up at the full moon and squint slightly at the markings, you can still see the Jade Rabbit.
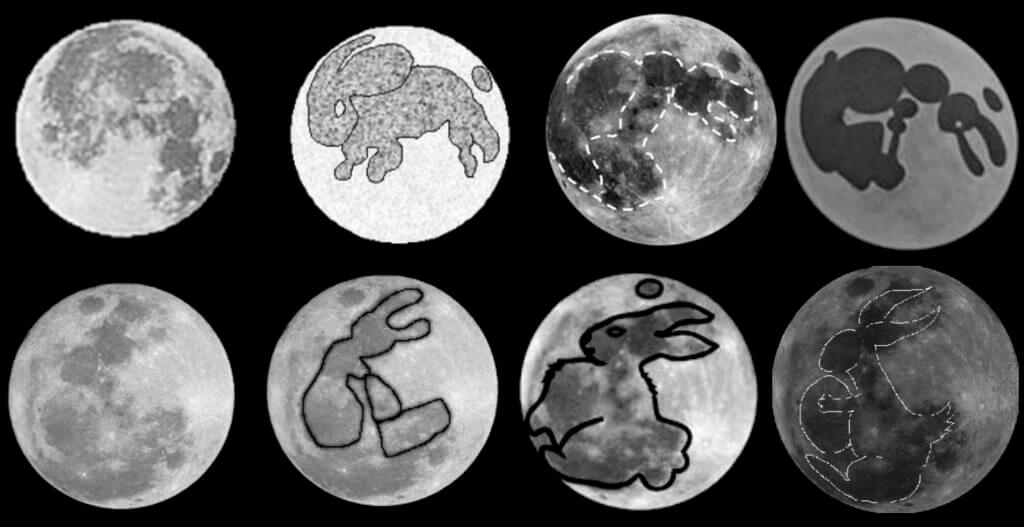
The Rabbit and the Moon
The association of the hare and the moon is common to folklore of Asia. In Chinese folklore, the hare is often portrayed as a companion of the Moon goddess Chang’e, 嫦娥, the Goddess of Immortality, constantly pounding the elixir of life or immortality for her. In other Chinese versions the rabbit pounds medicine for all the immortals.
For Japanese and Koreans, the Jade rabbit is pounding the ingredients for rice cake. In other versions, the rabbit, does not create elixir of life.

Another story tells of a white hare/rabbit serving Chang E, the goddess of the moon.
One Buddhist jataka – story about the Buddha in his earlier lives – tells that he was once a hare and sacrificed himself to the god Indra who was suffering from hunger.
As thanks for his selflessness, Indra then immortalized the hare by placing his image on the moon for all to see.
Mr. Mao Dun (a 20th-century Chinese novelist, cultural critic), once said,
“That the rabbits live on the moon and crows live in sun will always remain a mystery, simply existing there, without the point to be discussed about. “
Lady Chang E flying to the moon
Houyi was very much in love with his wife Chang E. Seeing that she was miserable as a mortal, Houyi set out to find a way back to the Heavens and to immortality. Travelling far to Kunlun Mountain, Houyi visited Xiwangmu (西王母), the Queen Mother of the West, who gave him a vial of elixir to share with his wife.
The vial contained enough elixir for both Houyi and his wife to become immortal but was the last of its kind, and the Queen warned Houyi that it must be shared between the archer and his wife as it was the last elixir for thousands of years.
On his return home, Houyi was obliged to pay his respects to the emperor of earth, but first he went straight home to give the vial to his wife for safekeeping.
However, one of Hou Yi’s students, Pang Meng or Feng Meng (逢蒙 féng méng), wanted the elixir for himself so when Hou Yi was out hunting one day, he tried to take it from Chang E.
Realizing Feng Meng’s intentions, Chang E quickly drank the elixir and began to rise to the Heavens. Not wanting to leave Hou Yi, she floated to the Moon – the closest place in Heaven to the earth – so that she could remain close to her beloved husband.

She would live in the moon palace and be called the moon goddess Chang’e 嫦娥 from now on.
Chang E “sacrifices” herself before Feng Meng could take the elixir.
This is, for many, the official story behind the celebrations for the Mid-Autmn Festival
After Chang E floated away, Hou Yi missed her intensely. He would often be found looking up to the moon (where it is said if you look close enough you can still see Chang E,) with teary eyes. And on each full moon he would place plates of her favorite foods out on tables for her. As time went on, other locals starting placing offerings on tables and prayed to Chang E, the Lunar Deity, Moon Goddess 嫦娥 for good luck and protection.

The other stories, the woodcutter Wu Gang吴刚 would live on the moon with Chang E.
He was banished to the moon because he had offended the gods. Wu Gang was only allowed to leave if he managed to cut down a tree that grew on the moon. He spent his time doing this, but each time he cut the tree down, it would grow back again, therefore condemning him to live on the moon forever.
Left alone on earth Houyi was later honored for his bravery and protection and welcomed back to the Heavens.
Over the centuries, the story of Chang E took many forms. Some versions of this tale say that Houyi built himself a palace on the sun as Yang (the male principle), while Chang E is Yin (the female principle).
Once a year, on the 15th day of the full moon, Houyi is able to visit his wife and on this night the moon is especially full and beautiful.
In other versions, Chang E took the elixir through an act of pure selfishness. Or that Chang E took the elixir to maintain her youth, she took it because Hou Yi was unfaithful to her, and there is even a version where Hou Yi claims himself king and becomes a tyrant so Chang E takes the elixir to ensure his reign would someday come to an end.
Chang E 嫦娥 and the Heavenly Dog
Tiangou 天狗 the Heavenly Dog, is a black dog that eats the moon or the sun. According to legends, as an interpretation of a lunar or solar eclipse.
Closely related to this story is the legend that when Chang E stole the immortal pills rewarded to her husband Hou Yi for shooting down the nine suns, Hou Yi’s hunting hound chased her all through her ascent up to the sky.
Hearing its bark, Chang E hid herself in the Moon. Meanwhile, all the hair on the hound’s body stood up erect and its body kept on expanding. Then in one motion, it leaped up and swallowed the Moon.
When the Heavenly King and Queen heard about this event, they sent the Heavenly Guards to apprehend the black dog. When it was brought forth, the Heavenly Queen recognized it as Hou Yi’s hunting hound and gave it the title of Heavenly Dog and the responsibility of guarding the Southern Heavenly Door.
As a result of the honor given to it, the hound spat out Chang E and the Moon. Thereafter, Change E made the Moon her home and became the Moon Goddess 嫦娥.
THE SUN
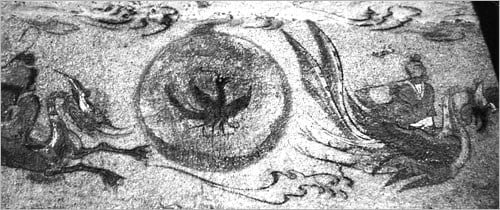
The three legged sun crows of art and myth

In Chinese mythology, the three-legged crow is called sanzuwu 三足乌; 三足烏; and also known as a “Yinyang” or “Sanhe”. Sanzuwu is believed to inhabit the sun and is a symbol of it. The three-legged crow represents good fortune and prosperity.
The three legs of the crow are said to symbolize the past, present, and future, and the bird’s ability to fly high in the sky is interpreted as the attainment of high goals and aspirations.
In traditional Chinese culture, the three-legged crow is often associated with the deity known as the “Red Crow,” who is said to bring good luck and prevent disaster. In some stories, the Red Crow is said to have the power to transform into other birds, such as a phoenix or a swallow, and to have the ability to fly between the heaven and earth.
Sanzuwu and the Queen Mother of the West 西王母 Xiwangmu
The sanzuwu, three-legged crow, is also depicted with the Queen Mother of the West 西王母; or Xi Wangmu, who is believed to be her messenger.
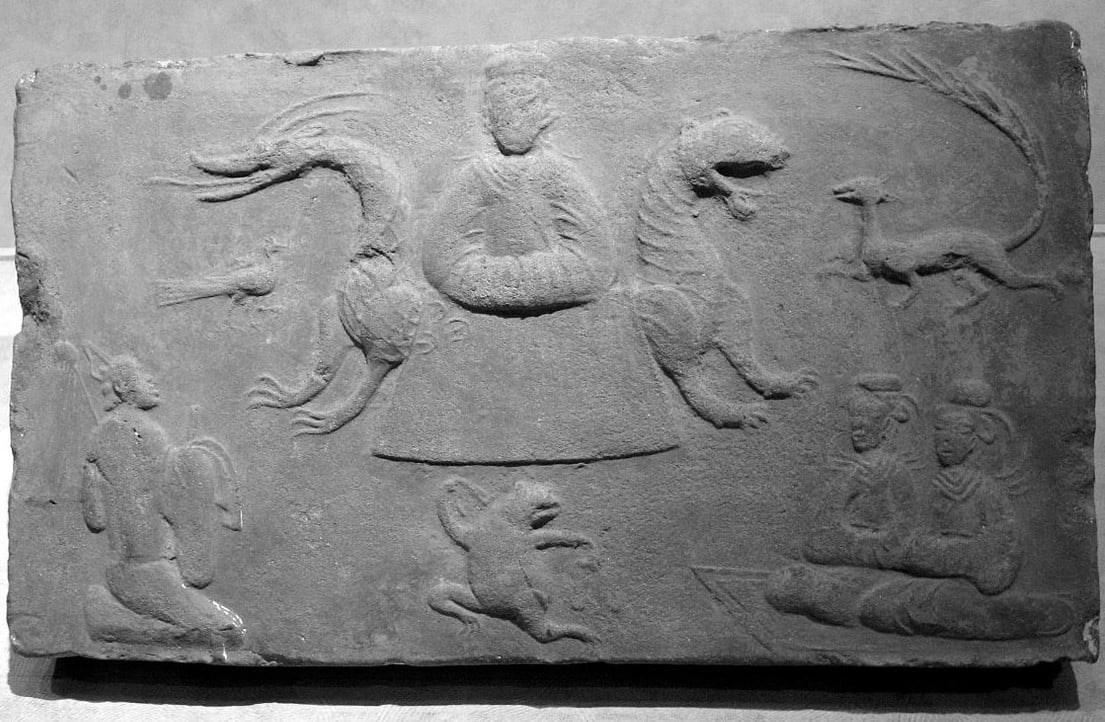

The Queen Mother of the West sits upon a throne, flanked by Tiger (east, spring, yang) and Dragon (west, autumn, yin). She is surrounded by a nine-tailed fox, two seated women, a leaping frog, a male attendant, and a three-legged crow. Eastern Han Dynasty, 25 AD – 220 AD.
Detail, the Queen Mother of the West with the three-legged crow.

Chu Ci (楚辞)
The Songs of the Chu-, is an anthology of Chinese poetry traditionally attributed mainly to Qu Yuan (屈原) (for whom the Dragon Boat Festival is celebrated) and his disciples. Chu Ci, as the book’s name indicates, is derived from the songs of the southern state Chu during the Warring States Period (476 BC – 221 BC).
In Chu Ci (楚辞), Chinese thought of the sun as a glowing chariot driven by 6 dragon horses across the sky and the Goddess Xihe (羲和) is the charioteer.

The Fusang tree, Sun Goddess Xihe who is going to hitch her Dragon Horse into the Sun Chariot, and Archer Yi who takes aim at the Sun Crows.
Sun chariot is under the giant Fusang mulberry tree, the home of the sun crows.
The ten suns burn earth
In other versions of this mythology, crows replaced the dragons to lead the chariot instead, taking Xihe’s orders.
According to Huai Nan Zi, there were originally ten suns, with crows living inside. Each day, one of the suns rose in the sky at a single point of time. They flew across the sky from the Fusang trees (扶桑树) in the east to the Ruo trees (若⽊木) in the west.
However, one day all the suns decided to rise all at once, which was devastating to the earth. So the God sent an archer named Hou Yi ( 后羿)to shoot down nine of them so that only one remained. The crows died therefore, giant-sized feathers falling down. The earth, finally, continued to stay safe.
“羿仰射⼗十⽇日,中其九⽇日,⽇日中九乌皆死,堕其⽻羽翼,故留其
⼀一⽇日也。”(Huainanzi, 淮南⼦子)
The Jade Emperor’s suns burn earth
Once upon a time, there were ten suns that took turns to circle the earth each day of the lunar week (10 days in the Chinese lunar calendar) – the suns took the form of black crows, with 3 legs, which rose in a mulberry tree in the east and landed in a mulberry tree in the west, before traveling home each night through an underground valley.
The suns were the children of the Jade Emperor but they were lonely in their work and one day, all ten of the suns came out together, scorching the earth and causing destruction.
The emperor of earth prayed to the Heavens for mercy and in anger, their father the Jade Emperor ordered them to behave. When they would not, he asked the great archer Lord Hou Yi 后羿 to reason with them and gave him leave to punish his sons. When Houyi saw the damage they had done he was very angry.
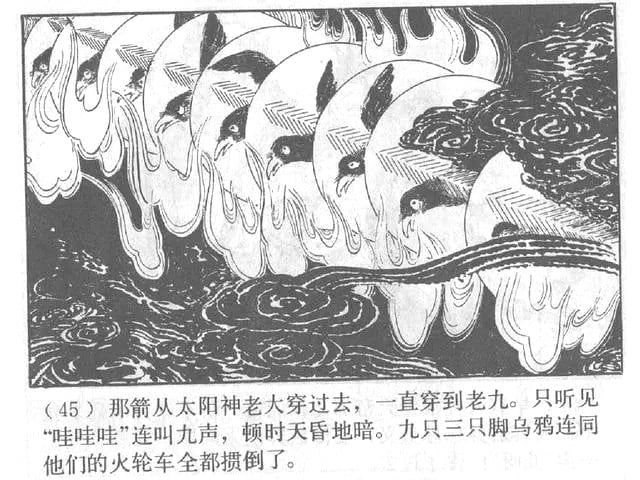
He tried to reason with the children but when they would not listen to him, Houyi shot down nine of the ten sons in desperation, leaving one behind to serve alone as the sun.
The Jade Emperor was very angry when he learned of the death of his sons. In a rage, he summoned Houyi and banished him and his wife Chang E to live as ordinary mortals on earth.
后羿射日 Hou Yi Shoots the Sun
As another variant of the story tells us, Di Qun (帝俊 dì qūn), an ancient God according to the Classic – Of Mountains and Seas (山海经 shān hǎi jīng), and his wife, Xi He (羲和 xī hé), had ten sons. Each son was a Three-Legged Golden Crow, a solar deity, charged with taking it in turns to travel across the sky in a chariot driven by their mother to nourish the earth.

One day the brothers decided to travel up into the sky together, with devastating results. Earth burned, the seas and plants dried up, and the people suffered.
Hearing of this, the Jade Emporer (玉帝 yù dì) ordered the Great Archer, Hou Yi (后羿 hòu yì) to take up his bow and shoot the disobedient Suns down. Hou Yi shot the Suns, one by one, until only one sun remained.
– Alternate versions of the myth 后羿射日 Hou Yi Shoots the Sun
When the Suns are hit in some versions they explode, in some they turn back in to Three-Legged Crows, and in others, they simply die.
In some versions Hou Yi stops shooting at 9 because he wants to leave one Sun to keep the earth warm, in another he only brought 9 arrows, and in another, Di Qun and Xi He beg Hou Yi to show mercy to their last living son.
Omens for the emperor
In ancient China, the solar and lunar eclipses were regarded as heavenly signs that foretell the future of the Emperor- predicting eclipses were of high importance for the state.

An eclipse was also an omen linked to natural disasters or deaths in the imperial family, it was a warning —for the Sun was the symbol of the Emperor according to traditional astrological theories. When an eclipse occurred, the Emperor would normally eat vegetarian meals, avoid the main palace, perform rituals to rescue the Sun and, sometimes, issue imperial edict to take the blame on himself.
The belief which linked celestial activity to that on earth is illustrated in an description of lunar behavior by a court astronomer, Shishen 石申, in the fourth century BC :
When a wise prince occupies the throne, the moon follows the right way.
When the prince is not wise and the ministers exercise power, the moon loses its way.
When the high officials let their interests prevail over public interest, the moon goes astray toward north or south.
When the moon is rash, it is because the prince is slow in punishing;
when the moon is slow, it is because the prince is rash in punishing.
In 2136 BC there was an unpredicted eclipse. Documentation about this event dates it as the earliest recorded eclipse in history but it also tells us about the fate of the court astronomers Xi 羲 and He 和 who failed to predict it in advance.
Given the belief that such celestial events reflected events on earth and should be predicted by the emperor, complete accuracy was expected of court astronomers, and failure meant – execution.
The Chinese have been hailed as some of the best astronomers and most detailed record-keepers; they would meticulously chart the courses of the celestial bodies and, in fact, did it so well that Astrology refers to their records to this very day.
Lunar and solar eclipses in ancient Astronomy
The ancient Chinese astronomer Shi Shen (fourth century B.C.) was aware of the relation of the moon in a solar eclipse, as he provided instructions in his writing to predict them by using the relative positions of the moon and sun.
The ‘radiating influence’ theory for a solar eclipse was opposed by the Chinese philosopher Wang Chong (27-97 CE), but he admits in his writing that it was nothing new. The Chinese astronomer and inventor Zhang Heng (78-139 CE) wrote of both solar eclipse and lunar eclipse in the publication of Ling Xian, 120 CE:
The sun is like fire and the moon like water. The fire gives out light and the water reflects it. Thus the moon’s brightness is produced from the radiance of the sun, and the moon’s darkness (pho) is due to (the light of) the sun being obstructed (pi).
The side which faces the sun is fully lit, and the side which is away from it is dark. The planets (as well as the moon) have the nature of water and reflect light. The light pouring forth from the sun (tang jih chih chhung kuang) does not always reach the moon owing to the obstruction (pi) of the earth itself—this is called ‘an-hsü’, a lunar eclipse.
When (a similar effect) happens with a planet (we call it) an occulation (hsing wei); when the moon passes across (kuo) (the sun’s path) then there is a solar eclipse (shih).
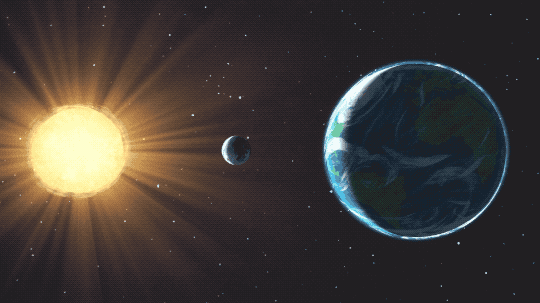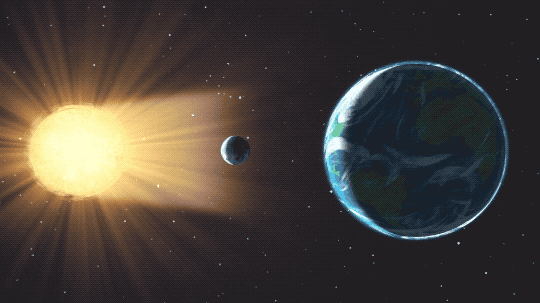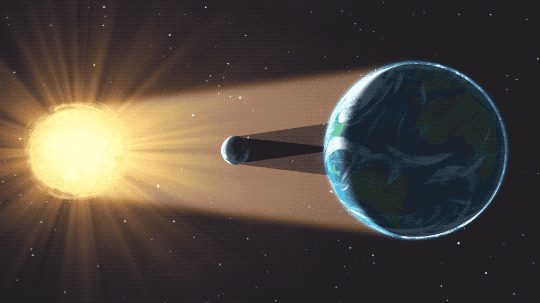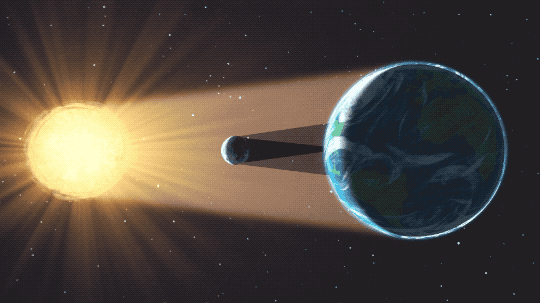
Furthermore, the later Chinese scientist Shen Kuo (1031-1095) used the models of lunar eclipse and solar eclipse in order to prove that the celestial bodies were round, not flat (which promoted spherical earth theory and went against flat earth theory).
He wrote of this in his Dream Pool Essays of 1088, relating back when the Director of the Astronomical Observatory had asked Shen if the shapes of the sun and moon were round like balls or flat like fans. Shen Kuo explained his reasoning for the former:
If they were like balls they would surely obstruct each other when they met. [said the director] I replied that these celestial bodies were certainly like balls. How do we know this?
By the waxing and waning of the moon. The moon itself gives forth no light, but is like a ball of silver; the light is the light of the sun (reflected).
When the brightness is first seen, the sun (-light passes almost) alongside, so the side only is illuminated and looks like a crescent.
When the sun gradually gets further away, the light shines slanting, and the moon is full, round like a bullet. If half of a sphere is covered with (white) powder and looked at from the side, the covered part will look like a crescent; if looked at from the front, it will appear round.
Thus we know that the celestial bodies are spherical.
When the director asked Shen Kuo why eclipses occurred only on an occasional basis while in conjunction and opposition once a day, he wrote:
I answered that the ecliptic and the moon’s path are like two rings, lying one over the other, but distant by a small amount.
(If this obliquity did not exist), the sun would be eclipsed whenever the two bodies were in conjunction, and the moon would be eclipsed whenever they were exactly in position.
But (in fact) though they may occupy the same degree, the two paths are not (always) near (each other), and so naturally the bodies do not (intrude) upon one another.
Historical observations of Solar Eclipses
Excerpt from the article:” Solar Eclipses in History and Mythology. Historical Observations of Solar Eclipses“.
Solar eclipses have been observed throughout history. Astronomy flourished in Mesopotamia, the plain between the two great rivers Tigris and Euphrates, in the dawn of civilization ( 7000 years ago). Like the Chinese and Egyptian astronomers, the Babylonian astronomers observed the motions of the Sun, Moon and planets carefully and kept records of the celestial events. They are also credited with remarkable contributions to ancient astronomy.
Ancient eclipse records made in China and Babylonia
Ancient eclipse records made in China and Babylonia are believed to be over 4,000 years ago.
Beginning as far back as 2400 BC, and especially during the Shang dynasty (1600 BC to 1046 BC)—a thousand years before the Chinese began to use paper—oracle bones were commonly used for divination.
Questions were posed, and animal bones or shells were then heated until they cracked into patterns which expert diviners were believed to “read.” The bones or shells were then inscribed with the interpretations and predictions.
Many astronomy-related inscriptions survive in these objects, but they are often cryptic and difficult to comprehend, sometimes lacking even the dates of the eclipses to which they refer.
“Because of the nature of the subject matter, oracle bones are not necessarily meant to be literal descriptions,” Odenwald explained.
Sten Odenwald , research professor, and of the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, was quoted in a July 29 National Geographic News story about the importance of solar eclipses in Chinese history.]
Peurbach, Georg von, 1423-1461, 176 h., [3]h. pleg. : il.; 8º Indexed In:
CCBE., S.XVI, G, 653 Public domain, edited.
Accuracy aside, the bones are the earliest known evidence of an interest in tracking eclipses.
Ancient China’s eclipse record keeping steadily improved over the centuries thanks to continued refinements in the calendar system driven by a search for signs that might tell the emperor’s future.
Systematic, dated eclipse records began in China in 719 BC
Astronomical computations enable astronomers to calculate the dates and paths of future and past eclipses with great accuracy. Some ancient eclipse records have been particularly significant to astronomers and historians as they enabled certain historical eras and events to be dated accurately. Astronomers can also examine ancient eclipse records to measure the rate of Earth’s spin about its axis over the past millenniums.

Astronomers from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) used Chinese observations of five solar eclipses that occurred between 1226 B.C. and 1161 B.C. and to study the rate of Earth’s axial rotation over the past 3,200 years. These eclipses were scratched on oxen shoulder blades in the Chinese city of Anyang.
By determining exactly when each of these eclipses was seen and where the Moon’s shadow fell on Earth in each eclipse, the scientists found that the day in 1200 B.C. was 0.047 second shorter than the present day.
By 20 B.C., Chinese astronomers realized the true nature of solar eclipses, and by 206 C.E., they were able to predict solar eclipses by analyzing the motion of the Moon.
Ancient eclipse records made in ancient Egypt and Greece
Recent research has demonstrated that solar eclipses had been depicted in the fascinating mythology of ancient Egypt, and produced evidence that the ancient Egyptians observed solar eclipses over 4500 years ago.
Dr. Mona Zoheir El-Shaieb, writes in BSU International Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, Vol.3 Issue 2 (2021) 12:
In the Prophecies of Neferti, preserved on papyrus St. Petersburg (formerly Leningrad 1116 B) dating from the 18th dynasty, relates the conditions that prevailed before the accession of Amenemhat I:
“The Sun disc, covered, shines not for people to see, one cannot live when clouds conceal it, all are numb from lack of it”.
“Ra … shines, that the hour may be told, but no one knows when noon occurs, for no one discerns his shadow, no man is dazzled by seeing [him] , there are no one whose eyes flow with water, because he is like the moon in the sky, … [then] his rays are in (men’s) eye as on former occasions”.
In the tomb of Meryre I the high-priest of Aton (TA 4), at Tell el-
Amarna, there is a unique and unusual solar scene:

This scene was believed, in McMurray’s opinion, to portray a total eclipse, and its most significant feature is the hindering of the sun’s rays heading towards Earth:
the two main groups of multiple arcs shown in the scene must match with the shadow bands seen just before and after totality, and their distinguish shape looks like the “diamond ring” effect (which occurs at the beginning and end of totality during a
total solar eclipse).
The Arab Egyptian astronomer Ibn Yunus (950-1009), was regarded as one of the greatest observational astronomers of his time, made important, precise observations of lunar and solar eclipses in Cairo.
Greek writers like Diodorus Siculus (200), admired the astronomical knowledge of the Egyptian priesthood and confirmed repeatedly its remarkable ability in predicting solar eclipses.
Plutarch related that the ancient Egyptians explained solar eclipses by the passage of the Moon between the Sun and the earth in daylight hours. There is evidence, admittedly disputed by some scholars, that an actual solar eclipse was reported in Egypt in the 9th century B.C. and again in 610 B.C.
The report of this latter eclipse has been attributed to Thales, though others, e.g., Herodotus, claim that Thales actually predicted an eclipse in 584 B.C. Thales, Greece’s first “philosopher”, was actually of Phoenician birth and spent seven years studying in Egypt. Greek commentators attribute Thale’s mathematical and astronomical knowledge to this apprenticeship in Egypt.
A fragment of a lost poem by Archilochus (ca. 680 BC–645 BC), who was a Greek poet and soldier, seems to clearly depict a total solar eclipse:
Nothing there is beyond hope,
nothing that can be sworn impossible,
nothing wonderful, since Zeus,
father of the Olympians,
made night from mid-day,
hiding the light of the shining Sun,
and sore fear came upon men.
Herodotus, the father of historiography, who lived in the 5th century BC, cited that Thales (ca. 624 BC-547 BC), the Greek philosopher, predicted the solar eclipse of 28 May 585 BC that put an end to the conflict between the Lydians and the Medes.
Herodotus wrote:
… day was all of sudden changed into night. This event had been foretold by Thales, the Milesian, who forewarned the Ionians of it, fixing for it the very year in which it took place.
The Medes and the Lydians when they observed the change, ceased fighting, and were alike anxious to have terms of peace agreed on.
Claudius Ptolemy (ca. 87-150 CE) wrote about eclipses in his epic work Almagest. His writings show that he studied the lunar orbit carefully and had a sophisticated scheme for predicting both solar and lunar eclipses.
Ancient eclipse records made in Arabia
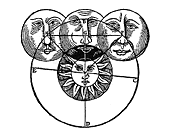
Peurbach, Georg von, 1423-1461 [1], 176 h., [3]h. pleg. : il.; 8º Indexed In: CCBE., S.XVI, G, 653. Public domain, edited.
One of the most important historical solar eclipses is that of the annular solar eclipse of 27 January 632. It was visible in Medina during the lifetime of Prophet Mohammad, Peace Be Upon Him (PBUH), and coincided with the death of his little son Ibrahim.
The Prophet stated explicitly and definitely that the eclipses of the Sun and the Moon are not bad omens, but are cosmic spectacles that demonstrate the might and knowledge of Allah the Great.
Ancient eclipse records made in India
The earliest written reference in Indian astronomy to a total solar eclipse is in the Rig Veda, an ancient collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns, one of the four sacred canonical texts in Hinduism, and one of the oldest known documents in the world.
Rishi Atri is said to have demolished the asura Swarbhanu to liberate the Sun from a total solar eclipse. The Rig Veda describes the occurrence of the eclipse, how the Sun suddenly disappeared in the daytime under the spell of the Asura (demon). The people and gods were scared but the Great Sage Atri saved the Sun and restored his full glory.
The verse translated by Griffith (1896), states:
“O Surya, when the Asura’s descendant Svarbhanu, pierced thee through and through with darkness, All creatures looked like one who is bewildered, who knoweth not the place where he is standing.
What time thou smotest down Svarbhanu’s magic that spread itself beneath the sky, O Indra, By his fourth sacred prayer Atri discovered Surya concealed in the gloom that stayed his function. […]
The Atris found the Sun again, him whom Svarbhanu of the brood Of Asuras had pierced with gloom. This none besides had the power to do.” [sic]
Griffith, R.T.H., Hymns of the Rigveda. Translated with a Popular Commentary. Volume I. Benares. 1896.
Based on the epic, Mayank Vahia, formerly of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research in Mumbai, and Mitsuru Sôma, a researcher at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, identify ‘Atri’s eclipse’ as occurring in Central Asia in either 4202 B.C. or 3811 B.C.
Both of these dates are earlier than the current record holders for the oldest mention of an eclipse — a clay tablet, unearthed in Syria, that recorded an eclipse in either 1375 B.C. or 1223 B.C., and a rock carving in Ireland that might reference an eclipse in 3340 B.C..
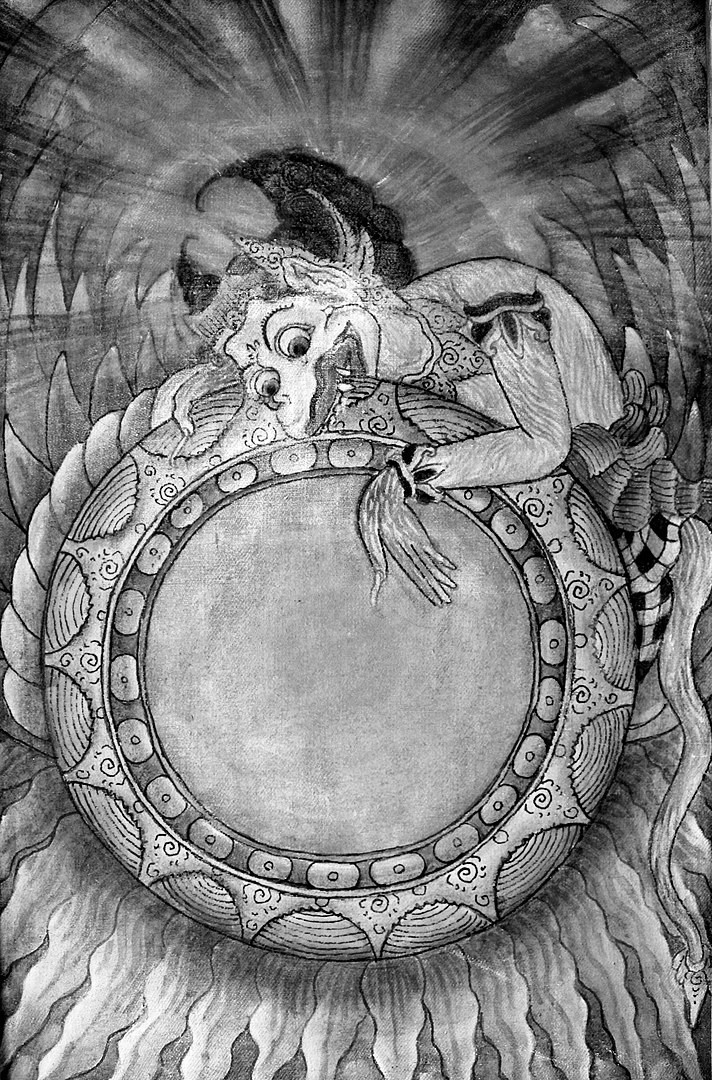

The rig-vedic verse is significantly older than the more common story of eclipses in India from the Samudra Manthan about Rahu and Ketu. The story refers to Indra and not Vishnu, further suggesting that the myth is younger.
Rahu and Ketu
When the asura named Rahu attempted to pose as a deva to receive amrita, the nectar of eternal life, Surya and Chandra, the deities of the Sun and the Moon, alerted Mohini, an incarnation of Vishnu. Mohini promptly employed her discus to behead the asura, but he had already partaken the nectar, and had become immortal. Rahu’s head was exiled to the heavens, and due to the two celestial deities’ part in his decapitation, he is said to occasionally swallow them whole for a given period of time, causing the solar and the lunar eclipse.
According to the Mahabharata epic, the sun god Surya is also described as an “enemy of Svarbhānu”. Svarbhānu was said to strike both the Sun and Moon with arrows, the celestial bodies being revived by Atri as in the Rigveda.
This story shows similarities to the Chinese story of Chang Xian the archer, who shots Tiangou or Tian Gou (“the heaven dog”), trying to devour the sun or moon.
The herd boy and the weaver girl or how the Milky Way was created

This story, of which there are many versions, goes back to the sixth century B.C. and can be found in the first known book of Chinese poetry, The Book of Songs (Shijing 诗经).
Avery long time ago, when the King of the Sky created the heavens, he decorated it with stars and asked his beautiful daughter to help him by weaving the clouds and mists. It was a long task and when the king noticed his daughter looking tired and drawn, he ordered her to take a break and go out to play among the stars.
The princess headed down towards the Milky Way to bathe, whereupon she came across a handsome herd-boy grazing his water buffalo by the banks of the stream. Distracted by the boy the princess lost track of time and returned home to her work long after the curfew her father had set.
The King, upon discovering the reason for her late return was very angry and forbade her to visit the boy again. In case she disobeyed him, the King poured thousands more stars into the Milky Way until it was no longer a stream but a flowing river that the princess and the herd-boy could not cross. Without a bridge, the two were stranded on opposite sides of the Milky Way forever more.
The Princess, who had fallen in love with the herd-boy, was distraught, and cried until her father relented. The King and his daughter reached an agreement that he would allow her to spend one day of each year with her herd-boy if she worked hard all year round.
To this day, on the seventh day of the seventh month of every year the King sends a flock of magpies over the Milky Way to form a bridge.
The weather must be clear on this evening or the lovers cannot cross the celestial river to meet each other. If it rains the pair must wait another year.
On a clear night you can see their two bright stars together in the sky. If it rains it is said that the drops falling to earth are the tears of the Weaver Girl Princess.
~ ○ ~
Keep exploring:
Works Cited & Multimedia Sources
- The Sun-Eating Dragon, Eclipse Stories, Myths, and Legends By Noel Wanner
- Astrology and Myth. https://web.archive.org/web/20220808101724/http://idp.bl.uk/4DCGI/education/astronomy/myth.html
- Barlow Joshua. Eat the Sun: Eclipse tales down the years.
- Eclipses in Ancient China Spurred Science, Beheadings? https://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2008/07/080729-china-eclipse_2.html
- FACTBOX: Solar eclipses, history and science. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-eclipse-asia-sb/factbox-solar-eclipses-history-and-science-idUSTRE56L08N20090722
- Historical observations of solar eclipses. http://www.bibalex.org/eclipse2006/HistoricalObservationsofSolarEclipses.htm
- http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Chinese_astronomy
- https://www.chinabeastsandlegends.com THANK YOU
- https://oldeuropeanculture.blogspot.com/2022/09/three-legged-crow.html Thank YOU
- https://news.cgtn.com/news/7a596a4d30557a6333566d54/share_p.html
- Jordan Hill, Cultures and stories along the path of totality. https://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2006/multimedia/storyteller.php
- Moonlakeku. Chinese Lore- Tian Gou (Heavenly Dog). 2015.
- The Chinese Sky
- Werner E. T. C. Myths and Legends of China. 2005. [EBook #15250]5]


