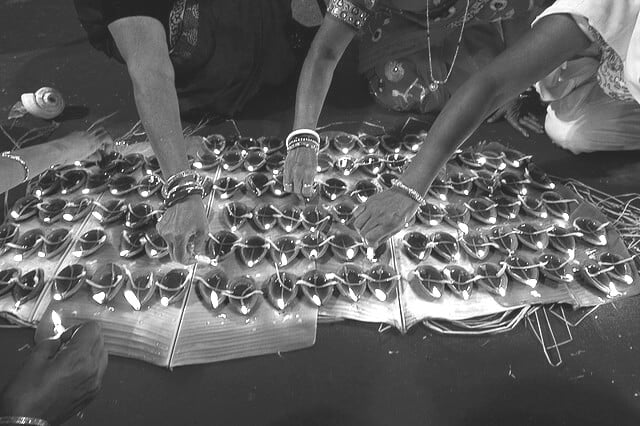
Discover legends, myths and folklore of the banana tree in India and its use in Indian culture. Offering and prayers to the Banana, is something which has been carried out since time immemorial.
In this Article
MUSA SAPIENTUM
Family: Musaceae
Sanskrit: Rambha, Kachii
Hindi : Kela
English: Plantain, Banana🍌
Offering and prayers to the Banana tree [Banana is not technically a tree, yet it is considered one because of its structure and size.] is something which has been carried out since time immemorial.
Since life cannot exist without trees, as a symbol of gratitude and gratification it is traditionally planted during festivities like: Vaisakha, Magha or Kartika Shukla Chaturdashi. It is said that worshiping the banana tree with flowers and fruits, – assures prosperity to the family.
The Banana, or Kadali plant
The Vishnu Parana, a salutation to Vishnu states:
“As the bark and leaves of the Kadali tree are to be seen in its stem, so thou are the stem of the universe and all things are visible in thee”.
Kadali plants, a variety of banana, mainly grown for temple offerings, are considered auspicious by the Hindus, particularly by the followers of Vishnu and Shiva, as the plant is believed to be the incarnation of Parvati, the wife of Shiva and Lakshmi, the wife of Vishnu.
The Kadali plants, particularly its leaves, are considered sacred for purposes of religious ceremonies and entire plants are placed at the entrance of houses for marriage, and also to decorate the panels erected for marriage ceremonies to symbolize fertility and plenty.
The Kadali fruit is offered to the deities at the temples. The plant is worshiped in the month of Kartik (Oct.-Nov.) by women desirous of having male progeny. The plant is a symbol of fecundity and a bride is given the banana fruit to assure her having male progeny.

A life size statue is made out of the Kadali plant and dressed like a bashful bride with Bilva (Aegle marmetos) fruits as her breasts, supported by a piece of sugar cane (Saccharum officinalis), The leaves of the plant are twisted like a bow, to represent the head and hair of the deity.
The nine plants that are used include:
- Banana with stem and leaves or plantain symbolically represents Brahmani.
- Kachvi (Arum colocasia) represents Kali.
- Turmeric (Curcuma indica) represents Durga.
- Jayanti (Hordeum vulgare) represents Karttiki.
- Wood apple or Bilva represents Shiva.
- Pomegranate (Punica granata) represents Raktadantika.
- Ashoka (Saraca indica) represents Sokarahita.
- Manaka, also known as Arum, represents Chamunda.
- Rice paddy (Oryza sativa), represents Lakshmi.
This plant deity is called Navapatrika, she is worshiped as Lakshmi and is also placed in front of a Bilva tree and worshiped for invocation of Durga, sometimes also associated with the Sun-God.
Durga or Lakshmi is worshiped mainly by women for the gift of a child’s prosperous life and a husband.

Oriyan tribal legend
According to an Oriyan tribal legend the plant was the creation of Bimma. As the plant bore nourishing fruit and every part of it was useful, Rama became jealous of Bimma’s creation and cursed it to die after producing only one bunch of flowers.
In reality, the Banana plant is a perennial plant and produces flowers and fruits season after season. The banana fruit is offered by certain tribes of Orissa and Madhya Pradesh to gods Kittungsum and Mardisum and is used in all religious and marriage ceremonies.
Gadaba legend
The reason why the Plantain bears fruit without pollination is described in a very interesting Gadaba legend.
Long, long ago, there were five sisters called Mango, Tamarind, Fig, Jamun and Plantain. When the sisters came of age, their father was worried about having to many children. When Plantain was asked what she desired, she said:“I certainly want children but not a husband. And I also want to get old soon and not have to wait for a long time”.
In course of time, Mango, Tamarind, Fig and Jamun got married and bore so many children that their husbands ran away in sheer fright. The girls in their next life were born as trees and bore many fruits which symbolically are the children they bore in an earlier life.
Plantain did not marry but produced children and grew old. And that is why, till today the Plantain plant bears fruit parthenogenetically, without pollination and the fruits do not bear any seeds.
Krishna and the Banana
A story in the Mahabharata [Sanskrit epic of ancient India] says that before the outbreak of the battle between the Kauravas and the Pandavas, Krishna went as a mediator.
The Pandavas did not want to go to war against their cousins, the Kauravas. But the Kauravas were adamant and would not listen to the sane advice given by Krishna, even after he had predicted the destruction of the entire race.
Defeated at his mission of bringing peace between the two rival sections of the family, Krishna went to the house of Vidura who was a half – brother, both to the Pandavas and the Kauravas.
Vidura was not at home and his wife Viduri, offered Krishna a Kadali fruit. She was so ecstatic by the presence of Krishna who had graced her threshold that absent mindlessly she threw away the Kadali- fruit and offered only the banana peel to Krishna.
Krishna had noticed this, but kept on eating the banana peel as it was offered to him with a pure heart and devotion.
Food Uses of the Banana
All banana plants can produce edible fruit, but the fruit taste, seediness, color, size and other characteristics depend on the species or variety.
Bananas can be peeled and eaten raw, baked peeled or unpeeled, made into a puree suitable for infants and peeled stems can be chopped and added to salads or steamed with other vegetables.
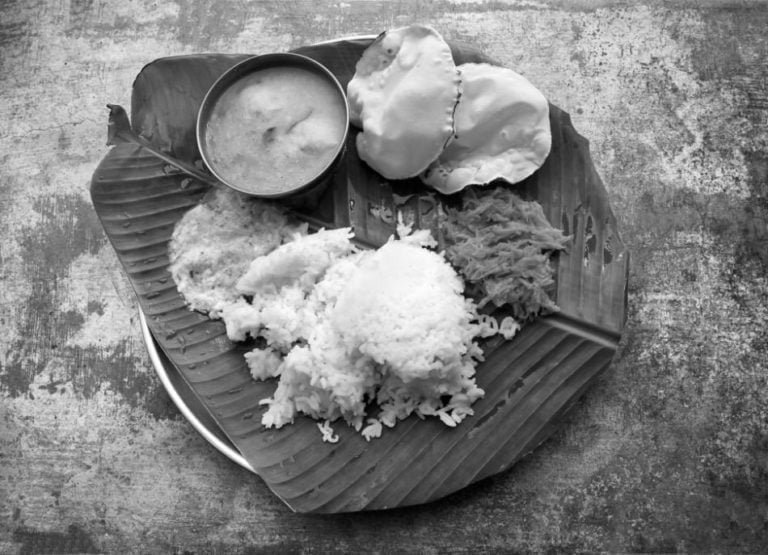

The leaf is the most sacred and would find its usage in all Vedic rituals. It is also considered to be the holiest plate to have meals on, which is why even today many south Indians serve their food on Banana leaves.
The leaves are not eaten but while steaming food some of the polyphenols are imparted to the food. In fact, in various puja ceremonies, the leaves are served as “Prasad”. It is believed that offering food on a Banana leaf pleases Lord Ganesha.
Ethnomedicinal uses of different parts of Musa Sapientum
Every part of the banana plant is used. The leaves are commonly as a packaging, for wrapping food and as an eye-shade or for protection from rain. The banana pseudostem can be utilized for its fiber. The pulp can be utilized to manufacture rope, paper, place mats and other goods, but the pseudostem is often most valuable economically if it is chopped and left in a field for its organic matter content.
The tree might have the following properties:
| Plant parts | traditional uses |
| Fruit | has a mild laxative property. used as a remedy of constipation in children. is believed to be helpful in curing diarrhea and dysentery. is believed to heal lesions in the intestine. part of diet of children suffering from malnutrition. one of the best sources of potassium, an essential mineral for maintaining normal blood pressure and heart function. |
| Flowers | Used to treat dysentery, ulcers, and bronchitis. Cooked, flowers are considered a good food for diabetics. |
| Sap | Chemically, banana sap has astringent qualities. In traditional medicine, the sap is used to treat a wide variety of ailments, including leprosy, hysteria, fever, digestive disorders, hemorrhage, epilepsy, hemorrhoids, and insect bites. |
| Roots and Seeds | used as a remedy of digestive disorders and dysentery |
| Banana seed mucilage | is given in cases of diarrhea. |
| Peel and Pulp | Scientifically shown to have both anti-fungal and antibiotic components. These structures have also been identified as containing the neurotransmitters norepinephrine, serotonin and dopamine. |
| Young leaves | placed as plaster on burns and other skin afflictions. |
| Ashes of the unripe peel and of leaves | are taken in dysentery and diarrhea and used for treating malignant ulcers. |
All parts of the banana have medicinal value.
Banana contains various bioactive compounds, such as alkaloids, phenols, flavonoids, tannins, and saponins, with reported therapeutic benefits, including antioxidant, anti-diabetic, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and anti-microbial activities.
The ethnomedicinal benefits of different parts of banana
| Part | Ailment | Ethnomedicinal belief |
Flowers | Diabetes | The fresh flower can be cooked and eaten to treat diabetes. The hypoglycemic effects of banana flowers have not been proved clinically. |
Dysentery | Cooked and eaten for bronchitis, dysentery and ulcers | |
Bronchitis | ||
Ulcers | ||
Menstruation PMS | The flowers are taken as an infusion in normal doses for painful menstruation. The vitamin B6 it contains regulates blood glucose levels, which can affect the mood. | |
| Plant sap | Stings and bites | Can be taken internally or applied externally to stings and bites. |
| Young leaves | Skin irritation | Can be used as a poultice for skin irritations. |
Ripe fruit | Depression | According to a recent survey undertaken by MIND amongst people suffering from depression, many felt much better after eating a banana. his is because bananas contain tryptophan, a type of protein that the body converts into serotonin, known to make you relax, improve the mood. |
| Anemia | High in iron, bananas can stimulate the production of hemoglobin in the blood and so helps in cases of anemia. | |
| Nerves | Bananas are high in B vitamins that help calm the nervous system. | |
| Constipation | High in fiber, including bananas in the diet can help restore normal bowel action, helping to overcome the problem without resorting to laxatives. | |
| Bladder infection | For bladder infection eat 3 to 4 bananas a day. | |
Colitis | Eating ripe bananas can prevent constipation, colitis, and heartburn | |
| Heartburn | Bananas have a natural antacid effect in the body, so if you suffer from heartburn, try eating a banana for soothing relief. | |
| Morning Sickness | Snacking on bananas between meals helps to keep blood sugar levels up and avoid morning sickness. | |
Laxative | Is laxative when eaten early in the morning. | |
Weakness | An excellent food for those anemic persons, having general weakness, jaundice, nervous breakdown, obesity, weak digestion and vitamin deficiency. | |
Obesity | ||
Jaundice | ||
Unripe fruit | Diarrhea | A night to get relief from constipation. If suffering from diarrhea you can use raw bananas. Boil the raw banana, mash it and add a pinch of salt and butter. Eat it to get relief from diarrhea. This is considered to be one of the most important health benefits of raw bananas. To increase the effectiveness of bananas for diarrhea, you can puree a small amount of ripe banana and add a teaspoon of honey to it. Apply this spread to a slice of well-done toast as the toast will help to absorb excess fluids within the gastrointestinal tract as well as provide bulk to the stools which helps to reduce the severity of diarrhea. |
Scurvy | Decoction of the unripe fruit is good for scurvy. | |
| Juice | Hemorrhages | The juice of the plant is taken to cure hemorrhages, cholera, epilepsy and hysteria (?). |
Cholera | ||
Epilepsy | ||
Hysteria ? | ||
| Hangover | Banana milkshake, sweetened with honey, calms the stomach and, with the help of the honey, builds up depleted blood sugar levels, while the milk soothes and re-hydrates the system. | |
Skin allergies | Mash one ripe banana in one cup of milk and drink it at least 2-3 times a day to treat skin allergies. | |
| Anti-wrinkle treatment | Banana or plantain has been widely used as an anti-wrinkle treatment. Mash 1/4 banana till it becomes a smooth paste. Cover your face with it and leave it for 15-20 minutes before rinsing with warm water followed by splashes of cold water. Pat it dry. You can also make a moisturizing face pack out of pureed bananas. Puree a small piece of banana and add enough fuller’s earth to it to make it a thick paste. Scrub your face well to get rid of the uppermost layer of grime and dead skin cells and then apply this paste to your face. Allow the paste to dry completely before washing it off with cold water. Fuller’s earth helps to absorb excess sebum from your skin and so this face pack will leave your skin fresh and smooth. Use this pack at least once a week to help provide your skin with the vitamins it requires to remain healthy and wrinkle free. If you have dry skin, you can add a teaspoon of coconut milk to this paste as coconut milk contains several healthy fatty acids that will help to fortify your skin and prevent wrinkles | |
| Trunk’s juice | Healthy growth of hair and hair loss | An extract of the trunk’s juice can be used to massage scalp to promote healthy growth of hair and preventing hair loss |
| Tuberculosis | Drinking extract from the stem attached to the banana cluster helps kill tuberculosis bacteria | |
| Inflorescence | Skin ulcers | The pounded inflorescence “puso” is used as poultice for skin ulcers and wounds |
Wounds | ||
Banana skin | Mosquito bites | Rubbing the affected area with the inside of a banana skin can be successful at reducing swelling and irritation. For warts, use the peel inside out and cover the wart by taping it. Once thepeel turns black remove and continue this for some weeks to get relief from wart. |
Warts | ||
| Poison ivy rashes | You can use banana peel for treating poison ivy rashes. Rub the peel inside out over the rashes; it soothes the skin to provide a cooling effect. If your skin is very sore, rubbing the peel on your skin may actually increase your discomfort. In such a case, you can use the blunt side of a knife to scrape the insides of the banana peel so that you get a thick grainy paste. Gently apply this paste to the affected portions of skin to help reduce the irritation and inflammation. | |
Bruises | Banana peel can be used if you have bruised yourself. Tape it overnight to see the positive results in the morning. If the bruising is rather severe, you can use this method twice or thrice a day to help reduce the discoloration and speed up the healing process. Make sure that you rinse and dry the area gently before applying a new piece of banana peel to your skin as this will increase the effectiveness of this treatment. | |
| Burnt banana leaves | Hiccups | Consuming two tablespoons of burnt banana leaves mixed with honey helps relief hiccups |
Note: This post does not contain medical advice.
Please ask a health practitioner before trying therapeutic products new to you.
If you do wish to experiment, I suggest doing further research.
~ ○ ~
Keep exploring:
Works Cited & Multimedia Sources
- Gupta Shakti M.Plant Myths & Traditions in India. 1968.
- Mahabharata.
- The Reasons Why We Worship Banana Tree.
- Traditional and Medicinal Uses of Banana, Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry Vol. 1 No. 3 2012. Volume 1 Issue 3.
- Photo Navapatrika.



